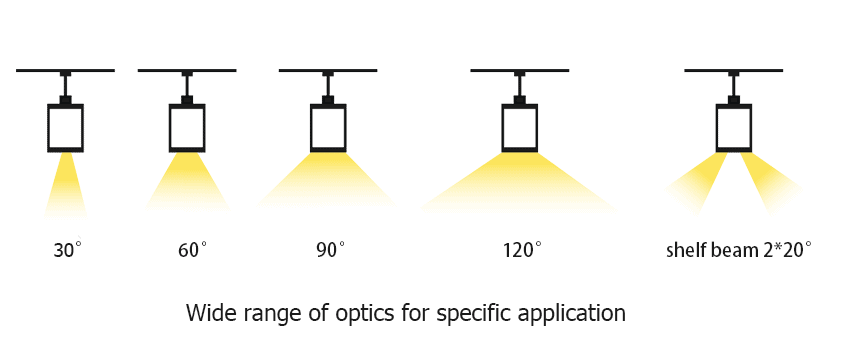
Introduction to Light Fixture Beam Angles
Lighting is one of the most important aspects of any interior or exterior space. It can create the perfect ambiance and set the tone for any occasion. However, choosing the right light fixture can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to selecting the right beam angle. With so many different options available, it can be difficult to know where to start.
In this guide, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview of light fixture beam angles, what they are, and how to choose the right beam angle for your specific needs.
What is a Light Fixture Beam Angle?
A light fixture beam angle refers to the angle at which light is emitted from the source, such as LED or other types of bulbs. This angle affects the distribution of light, illuminating specific areas with varying intensity levels, and creating a particular lighting effect.
Narrow, Medium, and Wide Beam Angles
Narrow Beam Angles (Spotlights)
Narrow beam angles, also known as spotlights, typically have a beam angle of 15-30 degrees. These angles provide focused and intense light, perfect for highlighting specific objects or architectural features.
Applications of Narrow Beam Angles
- Accent lighting: drawing attention to artwork, sculptures, or decorative elements
- Task lighting: providing focused light for workspaces, such as kitchens or workshops
- Outdoor lighting: illuminating pathways, signs, or landscape features
Medium Beam Angles (Floodlights)
Medium beam angles, or floodlights, range from 30 to 60 degrees. They offer a wider distribution of light than spotlights, making them ideal for general lighting purposes.
Applications of Medium Beam Angles
- General room lighting: creating a comfortable ambiance in living rooms, bedrooms, or offices
- Commercial spaces: providing balanced illumination in retail stores, restaurants, or galleries
- Exterior lighting: enhancing security and visibility in parking lots, building perimeters, or public spaces
Wide Beam Angles (Area Lights)
Wide beam angles, also known as area lights, have a beam angle greater than 60 degrees. These angles produce an even and diffused light, suitable for covering large areas.
Applications of Wide Beam Angles
- Industrial settings: illuminating warehouses, manufacturing plants, or large commercial spaces
- Outdoor areas: providing ample light for parks, sports fields, or large event venues
- Large indoor spaces: evenly distributing light in conference halls, auditoriums, or exhibition centers
Here is a table for the beam angle of NEMA classification:
| NEMA Beam Angle | Beam Description | Degree Level |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Long and narrow, suitable for lighting walkways, paths, and sidewalks. | 10° – 20° |
| Type II | Narrow, suitable for lighting smaller roads, alleys, and parking lots. | 30° – 45° |
| Type III | Medium, suitable for lighting wider roads, intersections, and large parking lots. | 70° – 90° |
| Type IV | Wide, suitable for lighting large areas such as parks, plazas, and campuses. | 100° – 120° |
| Type V | Very wide, suitable for lighting large open areas such as sports fields, airports, and industrial yards. | 120° or greater |
The degree levels provide a more specific measurement of the beam angle for each NEMA classification. By selecting the appropriate degree level, you can ensure that the outdoor lighting fixture provides the desired lighting coverage and intensity for the specific application.
Methods to measure the beam angle of a light source
There are several ways to measure the beam angle of a light source. Here are three common methods:
- Goniospectrometer: A goniospectrometer is a device that measures the intensity and direction of light emitted from a light source. The device rotates the light source while measuring the light output at different angles, allowing for the calculation of the beam angle.
- Field measurement: Field measurement involves using a light meter to measure the light intensity at different points in the beam spread. By measuring the light intensity at specific distances from the light source, the beam angle can be calculated using trigonometry.
- Manufacturer specification: The beam angle is often provided in the manufacturer’s specifications for the light source or fixture. This method is the simplest and most convenient, but it may not be as accurate as the other methods.
It’s important to note that different methods may provide slightly different measurements of the beam angle. It’s also important to consider the type of beam angle being measured, such as the full beam angle or the beam angle at 50% of the peak intensity. By understanding the different methods and types of beam angles, you can select the appropriate measurement method for your specific application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Beam Angle
When selecting the right beam angle for your lighting needs, consider the following factors:
- Purpose of Lighting: The intended use of the space will greatly influence the beam angle that is most appropriate. For example, a narrow beam angle would be ideal for highlighting artwork in a museum or gallery, while a wide beam angle would be better suited for a large open space such as a ballroom.
- Space Size: Consider the size of the area you’re illuminating to ensure proper light distribution.
- Mounting Height: The height of the ceiling will also play a role in selecting the right beam angle. In spaces with high ceilings, a narrow beam angle may be necessary to reach the desired area of focus. On the other hand, in spaces with lower ceilings, a wider beam angle may be more suitable to create an even wash of light.
- Desired Lighting Effect: Choose a beam angle that aligns with the overall aesthetic and ambiance you want to create. The desired mood or atmosphere of the space will also influence the selection of the appropriate beam angle. A warm, inviting atmosphere may be achieved with a wider beam angle, while a more dramatic or focused atmosphere may require a narrower beam angle.
- The Fixture Placement: The placement of the light fixture will also impact the beam angle selection. For example, if the fixture is mounted close to the wall, a wider beam angle may be necessary to cover the entire wall surface.
How to choose beam angle of LED Stadium light?
When selecting the beam angle for an LED stadium light, there are several factors to consider to ensure that the light provides adequate illumination to the playing area while minimizing glare and light spillage outside the stadium.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing the beam angle for an LED stadium light:
- Height of the stadium lighting poles: The height of the lighting poles will determine the beam angle required to achieve the desired lighting coverage and intensity. For higher poles, a narrower beam angle is needed to direct the light downwards, while a wider beam angle is suitable for lower poles.
- Type of sport: The type of sport being played will affect the beam angle required. For example, a sport with a smaller playing area, such as tennis, will require a narrower beam angle to provide adequate lighting to the playing surface, while a sport with a larger playing area, such as football or soccer, will require a wider beam angle to illuminate the entire playing area.
- Glare control: Glare can be a significant issue with stadium lighting, as it can affect the players’ visibility and cause discomfort to spectators. To minimize glare, it is important to select a beam angle that directs the light towards the playing surface while minimizing the light spillage outside the stadium.
- Energy efficiency: Energy efficiency is an essential consideration when selecting the beam angle for stadium lighting. A beam angle that is too wide may result in unnecessary light spillage outside the stadium, which wastes energy and increases light pollution.
In summary, when selecting the beam angle for an LED stadium light, consider the height of the lighting poles, the type of sport being played, glare control, and energy efficiency. By considering these factors, you can select a beam angle that provides optimal lighting for the playing area while minimizing the impact on the surrounding environment.
Conclusion
In summary, choosing the right beam angle for your light fixture is an important consideration when selecting lighting for any space. Factors such as the purpose of the space, ceiling height, fixture placement, and desired mood or atmosphere should all be taken into account when making your selection.
Furthermore, selecting the appropriate light bulb with the right color temperature and brightness level can greatly enhance the overall lighting effect.
We hope this guide has provided you with a better understanding of light fixture beam angles and how to choose the right one for your needs. By taking these factors into consideration, you can achieve the perfect lighting for any space.